When it comes to administering medications, the method of delivery plays a crucial role in how well a drug works in the body. Among the various options, sublingual and buccal medication administration are two methods that have gained popularity, particularly for patients who need quick relief or have difficulty swallowing pills. In this article, we’ll explore both methods, their differences, benefits, and potential drawbacks. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how these methods can be utilized effectively in medical treatments.
Sublingual Medication Administration
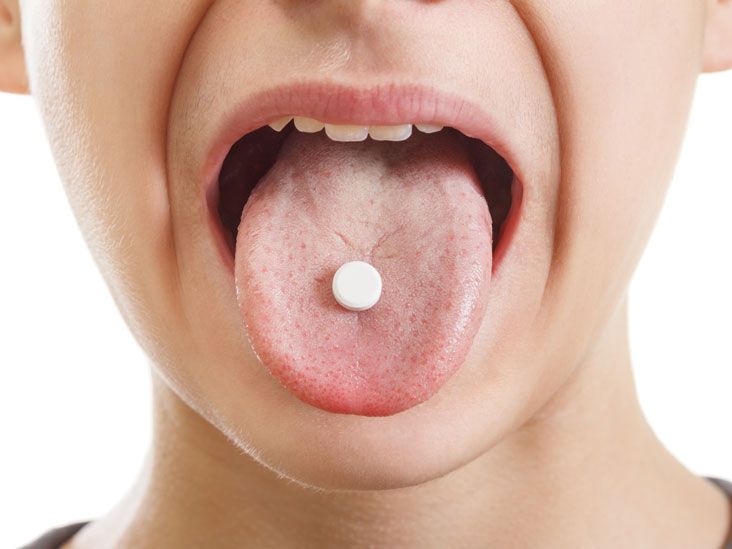
Sublingual medication administration involves placing the drug under the tongue. This method allows the medication to be absorbed directly into the bloodstream through the mucous membranes in the mouth. One of the biggest advantages of sublingual administration is that it bypasses the digestive system and liver, enabling the medication to enter the bloodstream more quickly. This is particularly beneficial for patients who require fast-acting relief, such as those with chest pain or severe nausea.
The sublingual route is often used for medications like nitroglycerin, which is prescribed for angina, and certain anti-nausea drugs. These medications are designed to dissolve quickly under the tongue, providing near-instant relief. Sublingual tablets or sprays are typically small and convenient, making them ideal for on-the-go use. However, patients must ensure that they don’t swallow the medication before it has dissolved, as this can reduce its effectiveness.
Advantages of Sublingual Medication
- Quick absorption: Drugs taken sublingually enter the bloodstream faster compared to oral medications, providing quicker relief.
- Bypasses the digestive system: This means that the medication isn’t broken down by stomach acids or liver enzymes, which could otherwise reduce its effectiveness.
- Convenient: Sublingual tablets are often small and easy to carry, making them ideal for patients who are on the go.
Buccal Medication Administration
Buccal medication administration, on the other hand, involves placing the medication between the gums and the cheek, where it can be absorbed through the buccal mucosa. Like sublingual administration, buccal delivery avoids the digestive system, but the absorption process is slower compared to sublingual medications. Buccal medications are typically designed to dissolve over a longer period, which makes them suitable for patients who require a steady release of the drug over time.
Common examples of buccal medications include certain hormone replacement therapies and some pain medications. These drugs are absorbed into the bloodstream through the lining of the cheek, and they may take a bit longer to work compared to sublingual medications. However, the advantage of buccal administration is that it can be used for extended-release medications, which provide long-lasting effects.
Advantages of Buccal Medication
- Steady release: Buccal medications often dissolve slowly, providing a consistent release of the drug over a longer period.
- Bypasses the digestive tract: Like sublingual medications, buccal drugs also avoid being broken down by stomach acids, ensuring better absorption.
- Ideal for long-term treatments: For medications that need to be released gradually, the buccal route is often the preferred option.
Key Differences Between Sublingual and Buccal Administration
While both sublingual and buccal medication administration methods allow for direct absorption into the bloodstream, there are several key differences:
- Absorption speed: Sublingual medications generally absorb faster than buccal medications due to their direct placement under the tongue and faster dissolution rate.
- Drug release: Buccal medications tend to release more gradually over time, whereas sublingual drugs often provide rapid, short-term relief.
- Application location: Sublingual medications are placed under the tongue, while buccal medications are placed between the gum and cheek.
Potential Drawbacks
Despite their advantages, both sublingual and buccal medication routes have some drawbacks. One of the main concerns is that the medications can be less convenient for patients who have difficulty using the methods properly, such as those with dry mouth or impaired motor function. Additionally, certain medications may not be suitable for these routes if they require high doses or if they need to be absorbed more slowly through the digestive tract.
Another potential drawback is that the absorption can be inconsistent depending on factors like saliva production and the patient’s ability to keep the medication in the correct position long enough to dissolve completely. While sublingual and buccal administration methods can be effective, they do require a certain level of compliance and technique from the patient.
Which Method Is Right for You?
Choosing between sublingual and buccal administration depends on the nature of the medication and the desired effect. If quick, short-term relief is needed, sublingual administration is often the best option. For medications that need to be released gradually over a longer period, buccal administration may be preferred. It’s important for patients to follow the instructions provided by their healthcare providers to ensure that the medication is used effectively and safely.
Conclusion
Sublingual and buccal medication administration are both effective methods for delivering drugs directly into the bloodstream while bypassing the digestive system. Sublingual medications offer rapid relief, making them ideal for acute conditions, while buccal medications provide a steady, extended release, making them suitable for long-term treatments. By understanding the differences and benefits of these two methods, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about the best medication delivery system based on individual needs.
Personal Experiences with Sublingual and Buccal Medication Administration
For many patients, switching to sublingual or buccal medications has been a game-changer, especially for those who need medications that act quickly or those who have trouble swallowing pills. One user, Sarah, shared her experience with using sublingual nitroglycerin for her heart condition. “I used to take oral medications for my chest pain, but I never felt they worked fast enough,” she explained. “When my doctor prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin, it was amazing how quickly it worked. Within minutes, I felt relief.” For Sarah, the sublingual route offered a quicker solution to her condition and gave her peace of mind knowing she could act fast if needed.
On the other hand, Michael, who uses a buccal medication for hormone therapy, shared how the buccal route provides more consistent treatment. “I’ve been on testosterone replacement therapy for several years, and the buccal method has been ideal for me. I don’t have to worry about taking a pill every day, and the effects last longer,” he said. For Michael, the gradual absorption through the buccal route aligns better with his long-term treatment plan.
Both patients highlighted the importance of following the instructions for correct administration to ensure the medication works as intended. “I’ve learned that I need to make sure I don’t swallow the sublingual tablet too soon or it won’t work properly,” Sarah advised. “And I’ve also had to be careful with buccal medications, making sure I place it in the right spot for absorption.”
Ultimately, both forms of medication administration have their benefits depending on the condition being treated and the desired results. It’s essential for patients to discuss their options with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of action. By considering both the rapid relief of sublingual medications and the gradual release of buccal treatments, patients can find the method that works best for their lifestyle and health needs.